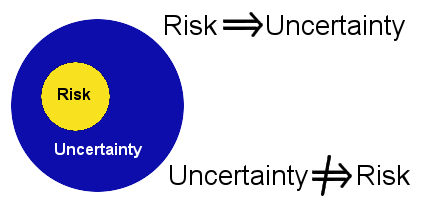
Successful software development involves understanding uncertainty, and uncertainty only comes from a few sources in a software project. The uncertainties of a software project increase with the size of the project and the inexperience of the team with the domain and technologies.The focus on this article is on uncertainty and not on risk. In part 1 we discussed uncertainty and in part 2 we discussed risk, so it should be clear that:
All risks are uncertain, however, not all uncertainties are risks.
 For example, scope creep is not a risk (see Shift Happens) because it is certain to happen in any non-trivial project. Since risk is uncertain, a risk related to scope creep might be that the scope shifts so much that the project is canceled. However, this is a useless risk to track because by the time it has triggered it is much too late for anything proactive to be done.
For example, scope creep is not a risk (see Shift Happens) because it is certain to happen in any non-trivial project. Since risk is uncertain, a risk related to scope creep might be that the scope shifts so much that the project is canceled. However, this is a useless risk to track because by the time it has triggered it is much too late for anything proactive to be done.
It is important to understand the uncertainties behind any software development and then to extract the relevant risks to monitor. The key uncertainties of a software project are around:
- requirements
- technology
- resources
- estimating the project deadline
Uncertainty in Requirements
There are several methodologies for capturing requirements:
- Business requirements document (BRD) or software requirement specification (SRS)
- Contract-style requirement lists
- Use cases (tutorial)
- User stories
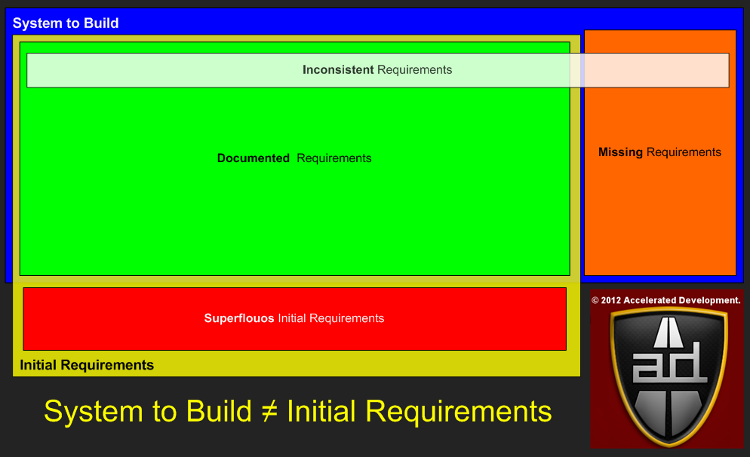
Regardless of the methodology used, your initial requirements will split up into several categories:
The blue area above represents what the final requirements will be once your project is completed, i.e. the System To Build. The initial requirements that you capture are in the yellow area called Initial Requirements.
With a perfect requirements process the Initial Requirements area would be the same as the System To Build area. When they don’t overlap we get the following requirement categories:
- Superfluous requirements
- Missing requirements
Superfluous initial requirements tends to happen in very large projects or projects where the initial requirements process is incomplete. Due to scope shift the Missing requirements category always has something in it (see Shift Happens). If either of these two categories contains a requirement that affects your core architecture negatively then you will increase your chance of failure by at least one order of magnitude.

For example, a superfluous requirement that causes the architecture to be too flexible will put the developers through a high learning curve and lead to slow development.
If scalability is a requirement of the architecture but it is missing during the initial architecture then you will discover that it is difficult and costly to add later.

The physical equivalent would be the apartment building here on the right. The foundation was insufficient to the needs of the building and it is slowly collapsing on one side. Imagine the cost of trying to fix the foundation now that the building is complete.
I’ve been in start-ups that did not plan for sufficient scalability in the initial architecture; subsequently, the necessary scalability was only added with serious development effort and a large cost in hardware. Believe me, throwing expensive hardware at a software problem late in the life cycle is not fun or a practical solution :-(.

The overlapping box, Inconsistent Requirements, is to categorize known and missing requirements that turn out to be in conflict with other requirements. This can happen when requirements are gathered from multiple user roles all of whom have a different view of what the system will deliver.
 It is much easier and faster to test your requirements and discover inconsistencies before you start developing the code rather than discover the inconsistencies in the middle of development. When inconsistencies are discovered by developers and QA personnel then your project will descend into fire-fighting (see Root cause of ‘Fire-fighting’ in Software Projects).
It is much easier and faster to test your requirements and discover inconsistencies before you start developing the code rather than discover the inconsistencies in the middle of development. When inconsistencies are discovered by developers and QA personnel then your project will descend into fire-fighting (see Root cause of ‘Fire-fighting’ in Software Projects).
The physical equivalent here is to have a balcony specified to one set of contractors but forget to notify another set that you need a sliding door (see right). When the construction people stumble on the inconsistency you may have already started planning for one alternative only to discover that rework is necessary to get to the other requirement.
Note, if you consistently develop software releases and projects with less than 90% of your requirements documented before coding starts then you get what you deserve (N.B. I did not say before the project starts 🙂 ). One of the biggest reasons that Agile software development stalls or fails is that the requirements in the backlog are not properly documented; if you Google “poor agile backlogs” you will get > 20M hits.
Requirements Risks
Some risks associated with requirements are:
- Risk of a missing requirement that affects the core architecture
- Risk that inconsistent requirements cause the critical path to slip
Uncertainty in Technology
Technical uncertainty comes from correctly using technology but failing to accomplish the goals as outlined by your requirements; lack of knowledge and/or skills will be handled in the next section (Uncertainty Concerning Resources). Team resources that don’t have experience with technology (poorly documented API, language, IDE, etc) does not constitute a technical risk it is a resource risk (i.e. lack of knowledge).
Technical uncertainty comes from only a few sources:
- Defective APIs
- Inability to develop algorithms

Unforeseen defects in APIs will impact one or more requirements and delay development. If there is an alternative API with the same characteristics then there may be little or no delay in changing APIs, i.e. there are multiple choices for XML parsing in Java with the same API.
However, much of the time changing to another API will cause delays because the new API will be implemented differently than the defective one. There are also no guarantees that the new API will be bug free.
Mature organizations use production APIs, but even then this does not protect you against defects. The best known example has to be the Pentium bug from Intel discovered in 1994. Although the bug did not seem to cause any real damage, any time you have an intermittent problem the source might always be a subtle defect in one of the APIs that you are using.
 Organizations that use non-production (alpha or beta) APIs for development run an extremely high risk of finding a defect in an API. This generally only happens in poorly funded start-ups where the technical team might have excessive decisional control in the choice of technologies.
Organizations that use non-production (alpha or beta) APIs for development run an extremely high risk of finding a defect in an API. This generally only happens in poorly funded start-ups where the technical team might have excessive decisional control in the choice of technologies.
The other source of technical uncertainty is the teams inability to develop algorithms to accomplish the software goals. These algorithms relate to the limitations of system resources such as CPU, memory, batteries, or bandwidth concern, i.e.:
- Performance
- Memory management
- Power management
- Volume of data concerns
 Every technical uncertainty is associated with one or more requirements. The inability to produce an algorithm to satisfy a requirement may have a work-around with acceptable behavior or might be infeasible.
Every technical uncertainty is associated with one or more requirements. The inability to produce an algorithm to satisfy a requirement may have a work-around with acceptable behavior or might be infeasible.
If the infeasible requirements prevents a core goal from being accomplished then the project will get canceled. If affected requirements have technical work-arounds then the project will be delayed while the work-around is being developed.
Technical Risks
Some risks associated with technology are:
- Risk that a defective API will cause us to look for another API
- Risk that we will be unable to find a feasible solution for a core project requirement
Uncertainty Concerning Resources
 When using the same team to produce the next version of a software product there is little to no resource uncertainty. Resource uncertainty exists if one of the following are present:
When using the same team to produce the next version of a software product there is little to no resource uncertainty. Resource uncertainty exists if one of the following are present:
- Any team member is unfamiliar with the technology you are using
- Any member of the team is unfamiliar with the subject domain
- You need to develop new algorithms to handle a technical issue (see previous section)
- Any team member is not committed to the project because they maintain another system
- Turnover robs you of a key individual
 Resource uncertainty revolves around knowledge and skills, commonly this includes: 1) language, 2) APIs, 3) interactive development environments (IDEs), and 4) methodology (Agile, RUP, Spiral, etc). If your team is less knowledgeable than required then you will underestimate some if not all tasks in the project plan.
Resource uncertainty revolves around knowledge and skills, commonly this includes: 1) language, 2) APIs, 3) interactive development environments (IDEs), and 4) methodology (Agile, RUP, Spiral, etc). If your team is less knowledgeable than required then you will underestimate some if not all tasks in the project plan.
When team members are unfamiliar with the subject domain then any misunderstandings that they have will cause delays in the project. In particular, if the domain is new and the requirements are not well documented then you will probably end up with the wrong architecture, even if you have skilled architects.
The degree to which you end up with a bad architecture and a canceled project depends on how unfamiliar you are with the subject domain and technologies being used. In addition, the size of your project will magnify all resource uncertainties above.
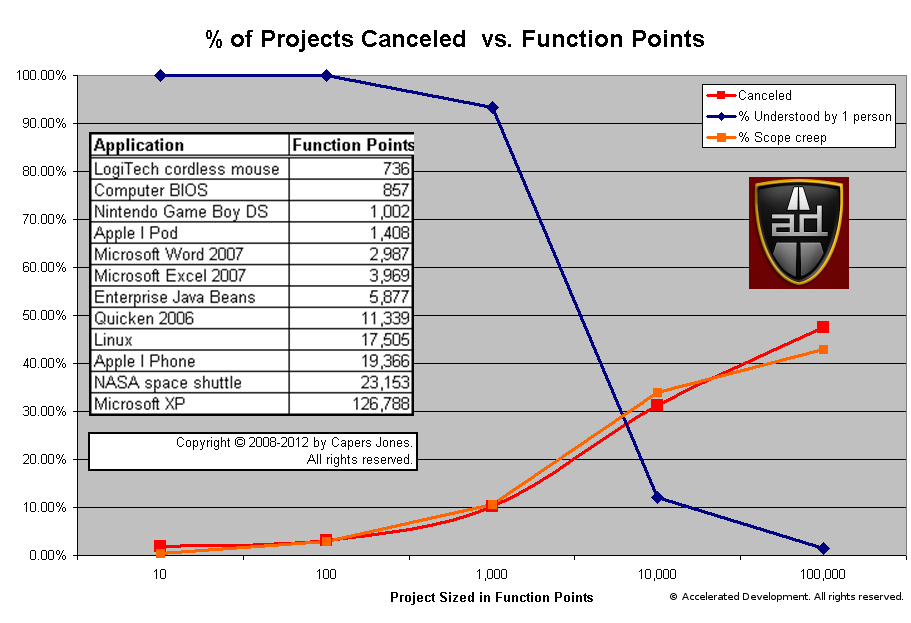
The majority of stand-alone applications are between 1,000 and 10,000 function points. As you would expect, the amount of the system that any one person can understand drops significantly between 1,000 and 10,000 function points. The number of canceled projects goes up as our understanding drops because all uncertainties increase and issues fall between the cracks. N.B. The total % of the system understood by a single person drops precipitously between 1,000 and 10,000 function points.
When there are team members committed to maintaining legacy systems then their productivity will be uncertain. Unless your legacy system behaves in a completely predictable fashion, those resources will be pulled away to solve problems on an unpredictable basis. They will not be able to commit to the team and multi-tasking will lower their and the teams productivity (see Multi-tasking Leads to Lower Productivity).
Resource Risks
Some risks associated with resources are:
- The team is unable to build an appropriate architecture foundation for the project
- A key resource leaves the project before the core architecture is complete
Uncertainty in Estimation
When project end dates are estimated formally you will have 3 dates: 1) earliest finish, 2) expected finish, and 3) latest finish. This makes sense because each task in the project plan can finish in a range of time, i.e. earliest finish to latest finish. When a project only talks about a single date for the end date, it is almost always the earliest possible finish so there is a 99.9% chance that you will miss it. Risk in estimation makes the most sense if:
- Formal methods are used to estimate the project
- Senior staff accepts the estimate
There are numerous cost estimating tools that can do a capable job. Capers Jones lists those methods, but also comments about how many companies don’t use formal estimates and those that do don’t trust them:
Although cost estimating is difficult there are a number of commercial software cost estimating tools that do a capable job: COCOMO II, KnowledgePlan, True Price, SEER, SLIM, SoftCost, CostXpert, and Software Risk
Master are examples.
However just because an accurate estimate can be produced using a commercial estimating tool that does not mean that clients or executives will accept it. In fact from information presented during litigation, about half of the cases did not produce accurate estimates at all and did not use estimating tools. Manual estimates tend towards optimism or predicting shorter schedules and lower costs than actually occur.
Somewhat surprisingly, the other half of the case had accurate estimates, but they were rejected and replaced by forced estimates based on business needs rather than team abilities.
Essentially, senior staff have a tendency to ignore formal estimates and declare the project end date. When this happens the project is usually doomed to end in disaster (see Why Senior Management Declared Deadlines lead to Disaster).
So estimation is guaranteed to be uncertain. Let’s combine the requirements categories from before with the categories of technical uncertainty to see where our uncertainty is coming from. Knowing the different categories of requirements uncertainty gives us strategies to minimize or eliminate that uncertainty.
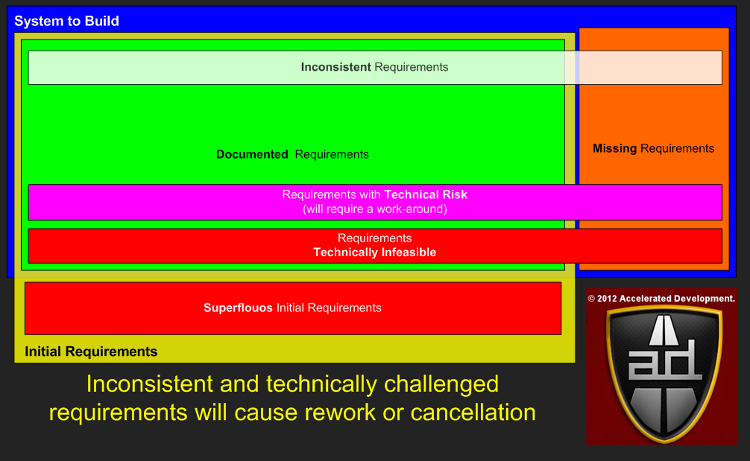
Starting with the Initial Requirements, we can see that there are two categories of uncertainty that can addressed before a project even starts:
- Superfluous initial requirements
- Inconsistent requirements
Both of these requirements will waste time if they get into the development process where they will cause a great deal of confusion inside the team. At best these requirements will cause the team to waste time, at worst these requirements will deceive the team into building the architecture incorrectly. A quality assurance process on your initial requirements can ensure that both of these categories are empty.
The next categories of uncertainty that can be addressed before the project starts is:
- Requirements with Technical Risk
- Requirements Technically Infeasible
Technical uncertainty is usually relatively straight forward to find when a project starts. It will generally involve non-functional requirements such as scalability, availability, extendability, compatibility, portability, maintainability, reliability, etc, etc. Other technical uncertainties will be concerned with:
- algorithms to deal with limited resources, i.e. memory, CPU, battery power
-
volume of data concerns, i.e. large files or network bandwidth
-
strong security models
- improving compression algorithms
Any use cases that are called frequently and any reports tie up your major tables are sources of technical uncertainty. If there will be significant technical uncertainty in your project then you are better off to split these technical uncertainties into a smaller project that the architects will handle before starting the main project. This way if there are too many technically infeasible issues then at least you can cancel the project.
However, the greatest source of uncertainty comes from the Missing Requirements section. The larger the number of missing requirements the greater the risk that the project gets canceled. If we look at the graph we presented above:
You can see that the chance of a project being canceled is highly correlated with the % of scope creep. Companies that routinely start projects with a fraction of the requirements identified are virtually guaranteed to have a canceled project.
In addition, even if you use formal methods for estimation, your project end date will not take into account the Missing Requirements. If you have a significant number of missing requirements then your estimates will be way off.
Estimation Risks
The most talked about estimation risk is schedule risk. Since most companies don’t use formal methods, and those that do are often ignored, it makes very little sense to talk of schedule risk.
When people say “schedule risk”, they are making a statement that the project will miss the deadline. But given that improper estimation is used in most projects it is certain that the project will miss its deadline , the only useful question is “by how much?“.
Schedule risk can only exist when formal methods are used and there is an earliest finish/latest finish range for the project. Schedule risk then applies to any task that takes longer than its latest finish and compromises the critical path of the project. The project manager needs to try to crash current and future tasks to see if he can get the project back on track. If you don’t use formal methods then this paragraph probably makes no sense 🙂
Conclusion
The main sources of uncertainty in software development comes from:
- requirements
- technology
- resources
- estimates
Successful software projects look for areas of uncertainty and minimize them before the project starts. Some uncertainties can be qualified as risks and should be managed aggressively by the project manager during the project.
Uncertainty in requirements, technology, and resources will cause delays in your project. If you are using formal methods than you need to pay attention to delays caused by uncertainties not accounted for in your model. If you don’t use formal methods then every time you hit a delay caused by an uncertainty, then that delay needs to be tacked on to the project end-date (of course, it won’t be 🙂 ).
If your project does not have strong architectural requirements and is not too big (i.e. < 1,000 function points) then you should be able to use Agile software development to set-up a process that grapples with uncertainty in an incremental fashion. Smaller projects with strong architectural requirements should set up a traditional project to settle the technical uncertainties before launching into Agile development.
Projects that use more traditional methodologies need to add a quality assurance process to their requirements to ensure a level of completeness and consistency before starting development. One way of doing this is to put requirements gathering into its own project. Once you capture the requirements, if you establish that you have strong architectural concerns, then you can create a project to build out the technical architecture of the project. Finally you would do the project itself. By breaking projects into 2 or 3 stages this gives you the ability to cancel the project before too much effort is sunk into a project with too much uncertainty.
Regardless of your project methodology; being aware of the completeness of your requirements as well as the technical uncertainty of your non-functional requirements will help you reduce the chance of project cancellation by at least one order of magnitude.
It is much more important to understand uncertainty that it is to understand risk in software development.
Appendix: Traditional Software Risks
This list of software risks courtesy of Capers Jones. Risks listed in descending order of importance.
- Risk of missing toxic requirements that should be avoided
- Risk of inadequate progress tracking
- Risk of development tasks interfering with maintenance
- Risk of maintenance tasks interfering with development
- Risk that designs are not kept updated after release
- Risk of unstable user requirements
- Risk that requirements are not kept updated after release
- Risk of clients forcing arbitrary schedules on team
- Risk of omitting formal architecture for large systems
- Risk of inadequate change control
- Risk of executives forcing arbitrary schedules on team
- Risk of not using a project office for large applications
- Risk of missing requirements from legacy applications
- Risk of slow application response times
- Risk of inadequate maintenance tools and workbenches
- Risk of application performance problems
- Risk of poor support by open-source providers
- Risk of reusing code without test cases or related materials
- Risk of excessive feature “bloat”
- Risk of inadequate development tools
- Risk of poor help screens and poor user manuals
- Risk of slow customer support
- Risk of inadequate functionality
 nfeasible software projects are launched all the time and teams are continually caught up in them, but what is the real source of the problem?
nfeasible software projects are launched all the time and teams are continually caught up in them, but what is the real source of the problem?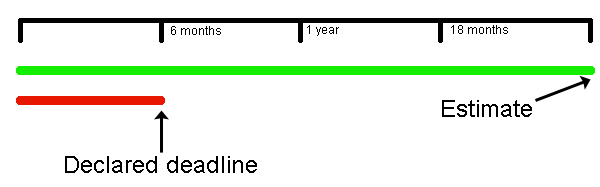 There is no schedule risk in an infeasible project because the deadline will be missed. Schedule risk only exists in the presence of uncertainty (see Schedule Risk is a Red Herring!!!)
There is no schedule risk in an infeasible project because the deadline will be missed. Schedule risk only exists in the presence of uncertainty (see Schedule Risk is a Red Herring!!!) When executives ignore formal estimates they get what they deserve. Formal estimates are ignored because executives believe through sheer force of will that they can set deadlines.
When executives ignore formal estimates they get what they deserve. Formal estimates are ignored because executives believe through sheer force of will that they can set deadlines. Improper estimation methods will underestimate a software project every time. Fast estimates will be based on what you can think of, unfortunately, software is not tangible and so what you are aware of is like the tip of an iceberg.
Improper estimation methods will underestimate a software project every time. Fast estimates will be based on what you can think of, unfortunately, software is not tangible and so what you are aware of is like the tip of an iceberg. Both executive ignorance and IT impotence lead to infeasible projects on a regular basis because of poor estimates and rejecting estimates; so there is no surprise here.
Both executive ignorance and IT impotence lead to infeasible projects on a regular basis because of poor estimates and rejecting estimates; so there is no surprise here. Possibly a greater share of problem is with IT management. After all, whose responsibility is a bad decision — the guys that know what the issues are or the ones that don’t.
Possibly a greater share of problem is with IT management. After all, whose responsibility is a bad decision — the guys that know what the issues are or the ones that don’t.








 This process is just like determining the cost for a house by the square footage and the quality, i.e. 2500 sq. ft at normal quality (~$200 per sq. ft.) would be approximately $500K, even without detailed blueprints. Very accurate estimates can be derived by sizing a project using function points.
This process is just like determining the cost for a house by the square footage and the quality, i.e. 2500 sq. ft at normal quality (~$200 per sq. ft.) would be approximately $500K, even without detailed blueprints. Very accurate estimates can be derived by sizing a project using function points.


 The waterfall methodology is widely attributed to
The waterfall methodology is widely attributed to